The ERC Guidelines 2021: Peri-arrest arrhythmias (Part 4/7)
Dr. Martin Fandler summarizes the key components, new issues and reconfirmed practices in the ALS management of tachycardia and bradycardia according to ERC 2021 Guidelines.
New guidelines available for cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the adult patient (ALS)
Dr. Martin Fandler (Sozialstiftung Bamberg, Bamberg) summarizes the key components, new issues and reconfirmed practices in the Adult Advanced Life Support management of tachycardia and bradycardia as announced in the new ERC 2021 Guidelines.
Made in cooperation with our partners from esanum.it
Early identification and treatment of life-threatening arrhythmias can prevent cardiac arrest or its recurrence. The ERC 2021 Guidelines include evidence and algorithms useful to the non-specialist ALS provider. If patients are stable, there is time to seek specialist medical attention.
Assessment and treatment of all arrhythmias are based on the patient's condition (whether stable or unstable) and the nature of the arrhythmia. Life-threatening situations that make a patient unstable include: shock, syncope, myocardial ischaemia, or severe heart failure.
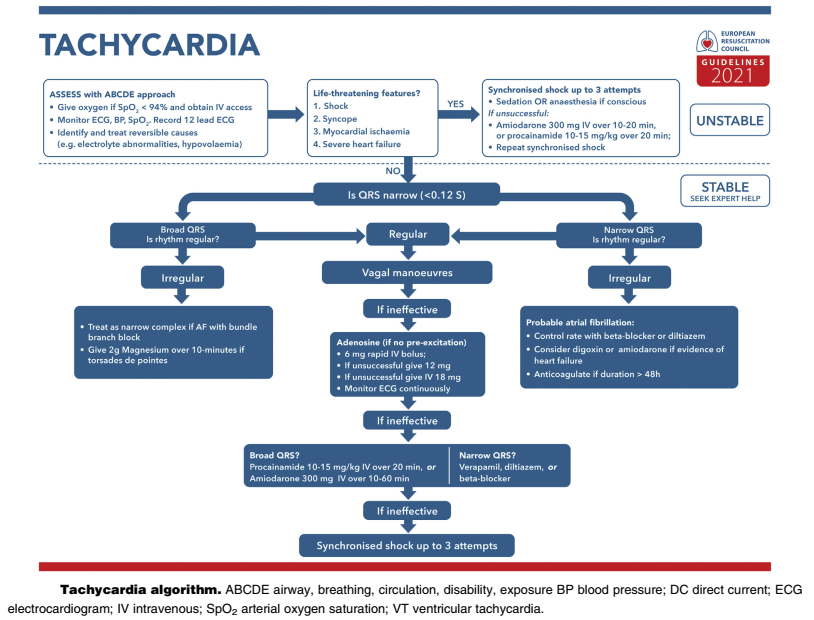
Peri-arrest rhythms: A new algorithm has been created for tachycardia
La prima domanda da porsi è “il paziente è in pericolo di vita"? (shock, sincope, ischemia miocardica, grave insufficienza cardiaca acuta). Nelle precedenti linee guida si parlava di "criteri di instabilità".
Se il paziente è stabile, si individuano 3 nuove categorie (nelle precedenti linee guida erano 4 categorie)
- Wide and irregular QRS: Atrial fibrillation with bundle branch block (treated as narrow and irregular QRS) or polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (PVT) (in case of peak torsion: 2g of magnesium sulphate in 10 min).
- Narrow/wide + regular QRS: Common vagal manoeuvres (see below), if ineffective adenosine, if ineffective move according to QRS length: wide QRS → amiodarone 300mg ev in 10-60 min or procainamide 10-15mg/kg ev in 20 min; narrow QRS → verapamil, diltiazem or beta-blocker. In case of further ineffectiveness, electrical cardioversion is performed (see below).
- Narrow and irregular QRS: Probable atrial fibrillation ( heart rate control with beta-blockers, if signs of heart failure digitoxin or amiodarone, anticoagulants if duration >48 h).
If the patient is unstable, electrical cardioversion is performed (unchanged procedure):
- R-wave-synchronous shock ("synchronised"), except in the presence of ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia.
- Analgesia (absence of pain) in conscious patients.
- Atrial fibrillation: 120-150 J (increase if unsuccessful).
- Atrial flutter/SVT (supraventricular tachycardia): 70-120 J (increase if unsuccessful).
- Ventricular tachycardia (with pulse): 120-150 J (increase if unsuccessful).
The adapted Valsalva manoeuvre in case of SVT (supraventricular tachycardia) is mentioned.
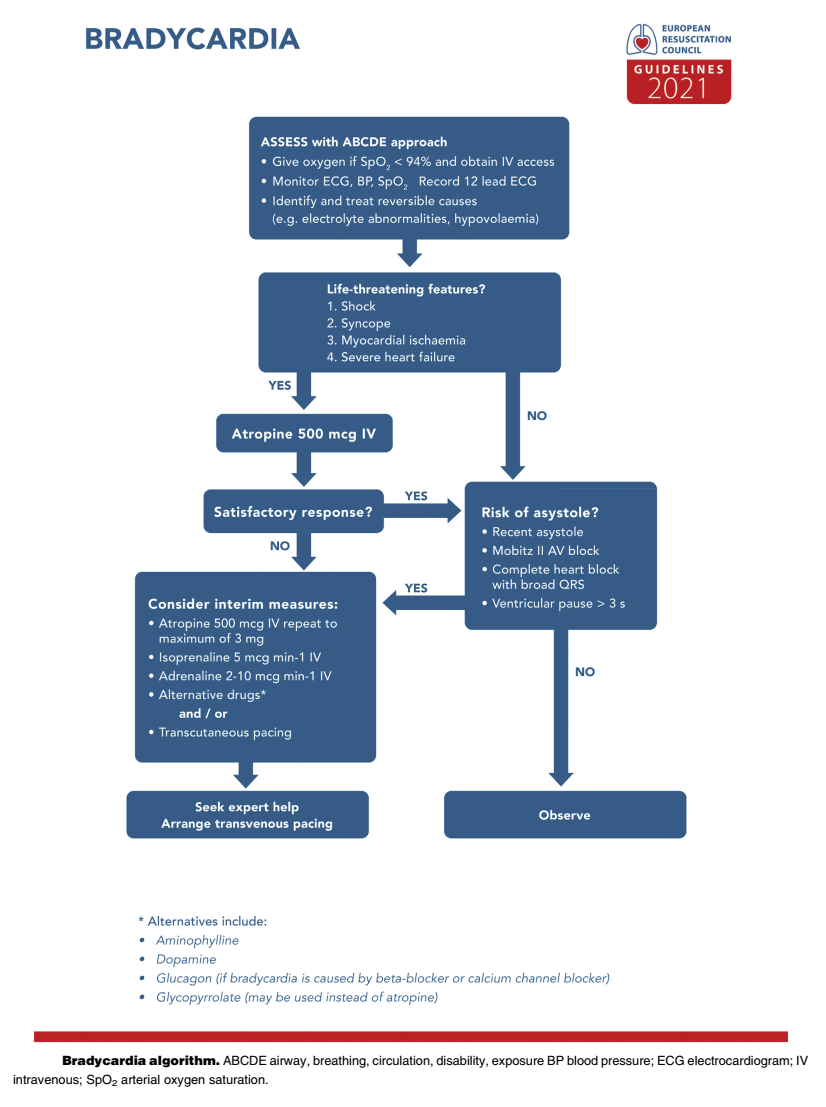
Peri-arrest rhythms: Bradycardia
- Unstable patient: Cardiac pacing (unchanged).
- Asystole: Attempt pacing only in presence of P wave (unchanged).
- Unchanged medication: First atropine (500 µg ev to be repeated up to a maximum of 3 mg); if ineffective: epinephrine (2-10 µg/min) or isoprenaline (5 µg/min). No atropine for heart transplant patients.
Editor’s Comment: In the prehospital/early shock room phase, adrenaline can also be administered as bolus; in this case, 1 mg adrenaline in 100 ml NaCl, then 1-2 ml ev slowly (= approximately 10-20 µg).
The 2021 ERC Guidelines can be downloaded here: New ERC Guidelines.
An overview of the most important ECR Guidelines 2021 changes is available in this esanum article series:
- The ERC Guidelines 2021 (Part 1/7)
- Main Changes (Part 2/7)
- Adult Advanced Life Support (ALS) (Part 3/7)
- Peri-Arrest Arrhythmias (Part 4/7)
- Cardiac Arrest in Special Circumstances (Part 5/7)
- Post-Resuscitation Care (Part 6/7)
- Resuscitation in Children (Part 7/7)
Sources:
1. Soar J, Böttiger BW, Carli P, Couper K, Deakin CD, Djärv T, Lott C, Olasveengen T, Paal P, Pellis T, Perkins GD, Sandroni C, Nolan JP. European Resuscitation Council Guidelines 2021: Adult advanced life support. Resuscitation. 2021 Apr;161:115-151. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2021.02.010. Epub 2021 Mar 24. PMID: 33773825.
2. Fandler M. Neue Reanimationsleitlinien 2021 (ERC) Zusammenfassung. Nerdfallmedizin.de. 25/03/2021